Little Snitch Network Monitor Sniffs Out Malware and Resource Hogs


Find out which applications are phoning home or collecting and sending data on your Mac using this handy utility.
Little Snitch Network Monitor is a macOS application that tells you exactly where your data is going to and coming from on the internet. This is a useful tool for rooting out malware on your computer or identifying which applications are hogging all your data. It can also tell you if a website is hijacking your computer to mine cryptocurrency, or otherwise redirecting your data to shady locales.
Little Snitch is easy to use and free to try. In this quick overview, I’ll show you how it works and what it does.

Where is my data going?
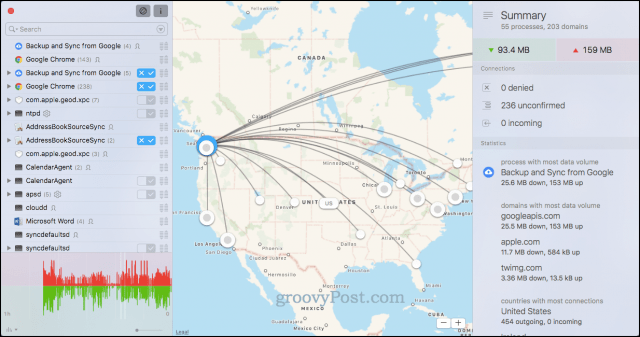
The most prominent element of the Little Snitch window is the global map that shows the geographic location of where your data is going to and coming from. In most cases, this won’t mean much—servers are located all over the globe, and just because your computer sends a packet or two to Romania or Switzerland isn’t particularly suspicious.


But if you are noticing strange traffic from an unknown application or a high volume of data being sent to a particular location, then it might be worth looking into. For example, it’s completely normal for Amazon Prime Video to be sending a bunch of data from Seattle since that’s where Amazon’s located. But it’d be more peculiar if your banking or financial application or website were sending data to North Korea at odd hours of the night.
How much data am I sending/receiving?
If it feels like you’re using up more data than you should on a monthly basis, Little Snitch can provide some insight. On the right-hand side is the summary which shows your overall data upload and download numbers. It also shows some statistics that highlight which connections are sending and receiving the most data.

For me, my Backup and Sync from Google is the major data hog. That’s pretty much expected since I use it to sync my photos and videos from iCloud to Google Photos. Red flags in this section would be unfamiliar applications sending lots of data, or applications sending lots of data when you’re not using them. This may be a case of bloatware or it could be malware or a virus. Or, it could be an application that you forgot you had and it’s working as designed.
Which programs are sending and receiving data?
On the left-hand side, you can see an exhaustive list of all connections sending amounts of data large and small. The bulk of the items here will be 100% normal system processes—stuff that Apple uses just to make macOS run smoothly. When you expand these out, you’ll notice they are phoning home to Apple.com, which means you can usually ignore it.


What’s interesting are the annoying third-party programs that occasionally send and receive data in the background. Many applications will have updaters or “helpers” that stay in contact with the developers servers for various reasons, such as checking for application updates. The amount of data is usually small, but if this bothers you, you can block these connections (see below).
Which websites are collecting my data or sending me data?
This one’s a bit eye-opening: when you visit a website, you’re making far more connections than just to the URL in your browser bar. Any given page may have dozens or more elements, scripts, and content from other servers. In some cases, this is perfectly normal. For instance, at groovyPost.com, we host our images on a content delivery network to help balance our server loads and make pages load faster depending on your geographic location.


But when you expand out your Google Chrome item, you’ll see pings from advertisers, analytics services, and other sites as well. Usually, this isn’t a cause for alarm—this is just the nature of the internet. Most websites and publishers are upfront about their use of third-party analytics services and advertising platforms.
That being said, there is potential for abuse. Last year, reports of websites hijacking your CPU to mine for Bitcoin came out. This is called “crypto jacking” and although it’s not really a privacy threat, most consider it unethical to hog your resources so publishers can profit. Little Snitch will tell you if a website is surreptitiously using your web browser to mine cryptocurrency by showing you traffic to domains like Coinhive.com.


Allowing and Denying Connections
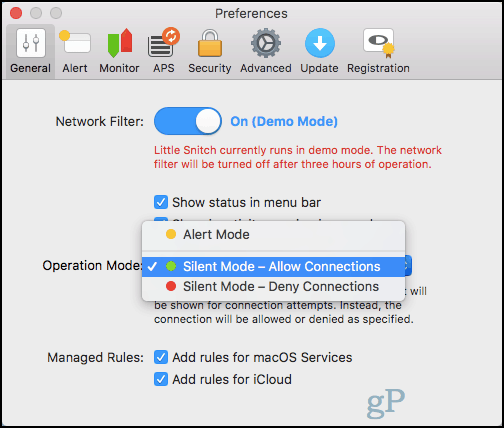
The recommended operation mode for Little Snitch is “Silent Mode – Allow Connections.” This lets you watch the traffic going across the transom without actively interfering with any of it. The other options: “Silent Mode – Deny Connections” and “Alert Mode” will quickly grind everyday internet activity to a halt.

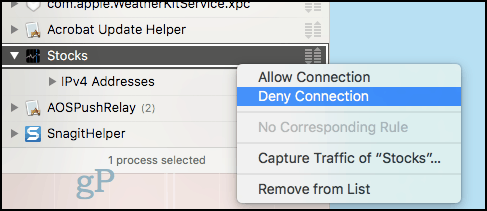
The idea is that if you do find a suspicious connection, you can choose to block it on a case by case basis. To do that, simply right-click the connection and choose Deny Connection. Little Snitch will block data from that connection.

Conclusion
Little Snitch is a handy application for monitoring and managing your incoming and outgoing network data on your Mac. The Demo Mode is pretty much unrestricted—pretty much the only limitation is that it will turn itself off every three hours, and you have to restore it. This means that if you suspect that you have malware on your computer or that a website is up to no good, you can use the Demo Mode of Little Snitch to investigate completely for free. If you do want to get a full license, it’ll cost you a little under $50.
Little Snitch does a great job of what it does. What it doesn’t do is monitor traffic on other devices on your network, including internet of things devices, smart home devices, voice-activated assistants, smart TVs, tablets, smartphones, etc. For those devices, you’ll need another solution which we’ll cover in a future post.
Let us know in the comments if you give Little Snitch a try.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply












